What are the different types of dredger winches?

The main types of dredger winches include ladder winches, anchor hoisting winches, side-wire winches, spud winches, towing winches, and special-purpose winches. Ladder winches control the movement of the dredger’s ladder arm, while anchor hoisting winches manage anchor positioning. Side-wire winches adjust the vessel’s lateral position, and spud winches raise or lower spuds for stability. Towing winches handle towing operations, and special-purpose winches support unique dredging tasks. Each dredger winch plays a vital role in supporting specific functions during dredging operations. The global market for marine winches, which includes dredger winches, reached $2.6 billion in 2024 and continues to expand as technology advances.
Key Takeaways
- Dredger winches come in several types, each designed for a specific task like controlling the ladder arm, managing anchors, adjusting vessel position, or towing heavy loads.
- Choosing the right winch depends on factors like load capacity, power source, safety features, and the dredging environment to ensure safe and efficient operations.
- Proper use of specialized winches improves dredging accuracy, stability, and safety while reducing maintenance and downtime.
Main Types of Dredger Winch

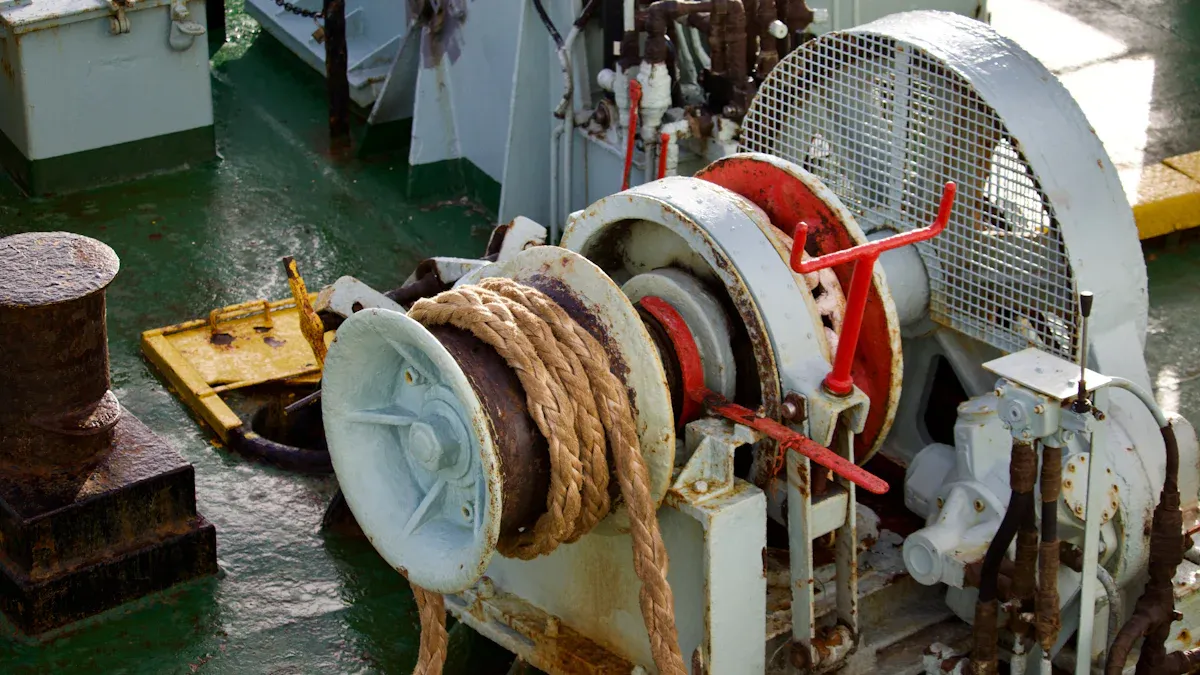
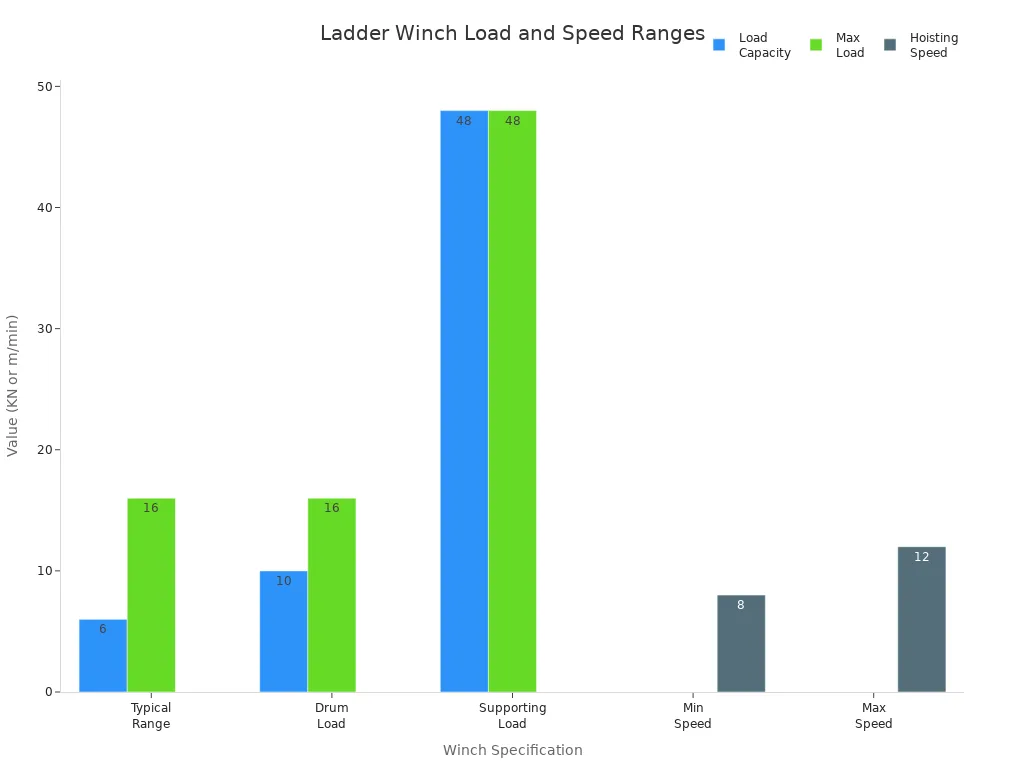
Ladder Winch
Ladder winches play a critical role in controlling the movement of the dredger’s ladder arm, which supports the excavation tool. Operators rely on these winches for frequent, precise adjustments to maintain optimal production and vacuum levels during dredging. The design of ladder winches often includes a V-belt drive system that acts as a slip clutch, protecting the mechanism from overload and breakage. This feature distinguishes ladder winches from other types, which typically use direct drive systems.
Note: Ladder winches use a 3-wire mooring system to keep the dredger stationary and allow for controlled vertical arc movements about the ladder hinge pin.
The following table highlights the primary mechanical and operational characteristics that set ladder winches apart from other dredger winch types:
| Characteristic | Ladder Winches (Chain Ladder Dredges) | Other Dredger Winch Types |
|---|---|---|
| Movement Type | Frequent, small, precise adjustments | Less frequent, larger movements |
| Control Mechanism | Mechanically controlled friction winches, responsive feathering | Less sensitive controls |
| Drive System | V-belt drive with slip clutch for protection | Direct drive, no slip clutch |
| Operational Role | Fine ladder position adjustments to maintain vacuum and production | Less delicate control needed |
| Digging Motion | Vertical arc about ladder hinge pin | Sideways or different arcs |
| Positioning System | 3-wire mooring for stationary operation | Different mooring systems |
Ladder winches are engineered for marine environments, with typical load capacities ranging from 6KN to 16KN and hoisting speeds between 8 and 12 meters per minute. Manufacturers use corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability in harsh conditions. Safety features such as overload protection and emergency stop buttons are standard.
Anchor Hoisting Winch
Anchor hoisting winches provide the pulling and braking force necessary to manage anchors during dredging operations. These winches ensure secure anchoring and precise vessel positioning, which is essential for maintaining stability while dredging. Operators benefit from robust safety features, including emergency release and overload protection, which reduce risks during anchor handling. The design of anchor hoisting winches allows them to adapt to various vessel types and operational conditions, even in challenging weather. Their reliability and strength make them indispensable for safe and efficient dredging.
- High pulling and braking forces enable safe anchor handling.
- Secure anchoring ensures vessel stability during dredging.
- Safety features minimize operational risks.
- Adaptability to different vessels and weather conditions.
- Robust construction supports reliable performance.
Side-Wire Winch
Side-wire winches adjust the lateral position of the dredger, allowing operators to move the vessel sideways with precision. These winches work in conjunction with the main mooring system to maintain the correct alignment of the dredger during excavation. By controlling the side wires, operators can counteract the effects of currents and wind, ensuring the dredger remains on course. Side-wire winches are essential for projects that require accurate positioning over extended periods.
Operators use side-wire winches to make incremental adjustments, which helps maintain the efficiency and accuracy of the dredging process.
Spud Winch
Spud winches operate in tandem with spuds—long, vertical steel shafts that anchor the dredger to the waterbed. These winches raise, lower, and reposition the spuds, providing the stability needed for safe and precise excavation. By adjusting the tension and position of the spuds, operators can keep the dredger stationary, even in strong currents or adverse conditions.
- Spuds anchor the dredger to the waterbed for stability.
- Winch systems reposition the barge and adjust anchoring tension.
- The combination of spuds and winches ensures the dredger remains stable and secure.
- Controlled positioning allows for accurate and safe excavation.
Towing Winch
Towing winches on dredgers are designed for heavy-duty marine applications, offering large pulling capacities and robust hydraulic or electric drives. These winches handle towing operations, assist tugboats, and manage heavy loads during dredging projects. Towing winches often feature multiple drums and spooling devices, enabling operators to manage large-diameter ropes safely and efficiently.
- Towing winches provide strong pulling power for heavy loads.
- High bollard pull capacities range from 5 to 250 tonnes or more.
- Hydraulic or electric drives ensure reliable performance.
- Multiple drums and spooling devices enhance operational safety.
- Specialized design differentiates towing winches from mooring winches or windlasses.
Special-Purpose Dredger Winch
Special-purpose dredger winches address unique operational requirements in challenging environments. Engineers design these winches with advanced hydraulic systems, ensuring quick and responsive tension management. The use of high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials guarantees durability and low maintenance. Integrated safety features, such as overload limit switches, protect equipment and operators. Special-purpose winches have demonstrated their value in demanding projects, such as maintaining stability and performance in turbid shallow waters.
Hydraulic systems in special-purpose winches allow operators to maintain control and stability, even in high winds and rough seas.
- Rugged construction withstands harsh marine environments.
- Bespoke designs meet specific project needs.
- Enhanced stability and control support performance in difficult conditions.
- Integrated safety features prevent equipment strain.
- Ease of operation ensures reliable results in demanding scenarios.
Choosing the Right Dredger Winch

Operation and Key Features
Operators select a dredger winch based on its operational role and technical features. Each winch type offers unique control options, such as manual levers or remote systems, to suit different vessel requirements. Safety features like overload protection, emergency stops, and load monitoring help prevent accidents. Manufacturers design winches with corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh marine environments. Power sources vary, including hydraulic, electric, pneumatic, or manual drives, each offering distinct advantages for specific tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Every winch type presents its own set of strengths. Hydraulic winches deliver high pulling power and smooth operation, making them ideal for heavy-duty dredging. Electric winches provide precise control and suit lighter loads. Pneumatic winches operate safely in hazardous environments. Manual winches offer simplicity and serve as reliable backups. However, operators must balance pulling power, speed, and control features to match the vessel’s needs.
Typical Applications
Dredger winches serve a range of applications. Ladder winches control the ladder arm for excavation. Anchor hoisting winches secure vessel positioning. Side-wire winches adjust lateral movement. Spud winches, especially in river dredging, raise and lower the ladder assembly, swing the dredge about a main spud, and relocate swing anchors. This method allows precise maneuvering in confined waterways. Towing winches handle heavy loads and assist with vessel movement. Special-purpose winches address unique project requirements.
Factors Influencing Selection
When choosing a dredger winch, operators consider several factors:
- Define the application purpose, such as anchoring, towing, or cargo handling
- Assess load capacity and line pull requirements
- Evaluate the operating environment, including weather and corrosion potential
- Select the appropriate power source and control system
- Ensure safety features are present
- Consider brand reputation, warranty, and after-sales support
- Verify compliance with industry standards and certifications
Each dredger winch type offers unique features and operational roles. Selecting the right dredger winch for the vessel and dredging task leads to:
- Improved handling of environmental and soil conditions
- Enhanced stability, safety, and operational control
- Reduced downtime and maintenance needs
Industry best practices recommend evaluating equipment compatibility, maintaining rigorous inspection routines, and partnering with reputable suppliers. Careful selection ensures optimal performance and project success.
FAQ
What is the main difference between hydraulic and electric dredger winches?
Hydraulic winches deliver higher pulling power for heavy-duty tasks. Electric winches provide precise control and suit lighter loads. Operators select based on project requirements.
How often should operators inspect dredger winches?
Operators should inspect winches before each operation. Regular monthly maintenance checks help ensure safety and extend equipment lifespan.
Can one winch type replace another in dredging operations?
| Winch Type | Replacement Feasibility |
|---|---|
| Ladder Winch | No |
| Anchor Hoisting | No |
| Side-Wire Winch | No |
Each winch serves a specific function. Operators cannot substitute one type for another.