2026 Marine Deck Crane Industry Trends: Intelligent and Green Dual Engines

“Intelligent and Green Dual Engines” signifies the powerful convergence of advanced smart technologies and sustainable environmental practices for Marine Deck Cranes. These dual forces are paramount for driving innovation and operational efficiency within the industry. The market’s robust growth underscores their significance:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Projected Market Size (2025) | USD 5.04 Billion |
| Projected Market Size (2032) | USD 7.40 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 5.6% |
This trajectory highlights the critical role of intelligence and sustainability in shaping the future of marine operations.
Key Takeaways
- Smart technology makes marine cranes work better and safer.
- New green methods help marine cranes protect the environment.
- These changes make marine operations more efficient and responsible.
Current Landscape of Marine Deck Crane Technology
Present State of Automation and Digitalization
Today’s marine deck cranes incorporate foundational automation and digitalization. Operators often utilize remote control systems for basic crane functions. Sensors provide real-time data on load weight and boom position, enhancing operational awareness. Digital interfaces display critical operational parameters, assisting crane operators in their tasks. These systems improve efficiency and reduce manual effort. However, current automation primarily focuses on individual crane functions rather than fully integrated, autonomous operations. Data collection occurs, but advanced analytics for predictive insights remain largely untapped in many standard models.
Existing Environmental Considerations in Marine Deck Cranes
Environmental concerns already influence marine deck crane design and operation. Manufacturers and operators adhere to various regulations to minimize ecological impact. These mandates guide operational practices and equipment specifications.
- Clean Water Act (CWA): This act regulates activities within U.S. waters that could affect water quality.
- Marine Mammal Protection Act (MMPA): This act governs activities within U.S. waters that could harm marine life.
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) guidelines: These international guidelines aim to protect the marine environment.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Projects require these assessments before commencement to ensure minimal harm to surrounding waters.
- Local and International Environmental Laws: Compliance is necessary, as these laws vary by project location.
These regulations drive the adoption of more efficient hydraulic systems and better waste management practices onboard vessels. The industry continuously seeks ways to reduce its environmental footprint, even with current technological limitations.
Intelligent Technologies Driving Marine Deck Crane Evolution

The marine industry is rapidly adopting intelligent technologies. These innovations are transforming how marine deck cranes operate. They enhance efficiency, safety, and overall performance.
AI and Machine Learning Integration in Marine Deck Cranes
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are revolutionizing marine deck crane operations. These technologies allow cranes to perform tasks with greater precision and accuracy. AI algorithms analyze real-time data to optimize crane movements. They reduce errors and improve overall efficiency. AI also enhances safety by detecting potential dangers like obstacles or unstable loads. This reduces risks for human operators and minimizes damage.
Specific AI algorithms find application in various aspects of crane operations:
- Computer Vision: This technology classifies containers live. It detects placards, reads container IDs, and cross-checks cargo types against manifests. This enables automatic assignment to appropriate zones and routing via Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).
- Pose Estimation Technology: This provides real-time container positioning and micro-adjustments. It uses stereo cameras to detect container edges and track movement in six degrees of freedom. It predicts swing patterns and offers micro-adjustments to the crane spreader for precise alignment.
- Predictive Container Stacking: This employs 3D neural networks, specifically 3D-CNN models, to forecast pickup timing. These models predict container pickup likelihood based on trucking schedules, customs alerts, and historical patterns. This allows placing containers likely to leave soon on top of stacks.
AI also enables predictive maintenance. It continuously monitors crane performance and detects signs of wear. This allows for proactive repairs and reduces downtime. Operational flexibility also improves. AI algorithms can recognize and handle different cargo types without manual reprogramming. Furthermore, automation contributes to environmental sustainability. It optimizes energy consumption, reduces fuel use and emissions, and promotes eco-friendly practices. AI integration significantly accelerates productivity and safety in port operations. It drives container cranes towards autonomous operations. It also assists crane operators by improving graphical guidance and enhancing safety through better risk detection and more responsive warnings.
Advanced Automation and Robotics for Marine Deck Cranes
Advanced automation and robotics are pushing the boundaries of marine deck crane capabilities. These systems move beyond basic remote control. They enable more complex and autonomous operations. Robotic components can execute repetitive tasks with high precision. This frees human operators for supervisory roles or more complex decision-making. Automated systems can handle cargo loading and unloading sequences with minimal human intervention. This increases throughput and reduces operational costs.
Robotics also plays a role in inspection and maintenance. Drones or robotic arms can inspect hard-to-reach crane components. They identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach enhances safety and extends equipment lifespan. The integration of these advanced systems leads to a more streamlined and efficient workflow on vessels and in ports.
IoT Connectivity and Data Analytics for Marine Deck Cranes
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects marine deck cranes to a vast network of sensors and data streams. This connectivity allows for real-time data collection from various crane components. These sensors gather critical operational parameters. Data analytics then processes this information. It provides valuable insights into crane performance, health, and operational efficiency.
Critical data points for IoT connectivity include:
| No. | Parameter | Default State | Operational State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fire Alarm | Normal | Alarm |
| 2 | Brake Valve Status | De-energized/Engaged/Idle | Energized/Disengaged/In Operation |
| 3 | Hydraulic Oil Tank Level | Normal | Low (Alarm) |
| 4 | Operator Joystick Output Voltage | 6 VDC (Neutral) | (0–6 VDC) (Lowering), (6–12 VDC) (Hoisting) |
| 5 | Hydraulic Oil Feed Pressure | 0 bar (Idle) | (20–40 bar) (Normal), (<20 bar) (Alarm), (>40 bar) (Alarm) |
| 6 | Hydraulic Oil Temperature | Ambient Temp. (Idle) | (<60 °C) (Normal), (>60 °C) (Alarm) |
| 7 | Hoisting Load Pressure | 0 bar (Idle) | (<200 bar) (High Speed), (>200 bar) (Low Speed) |
| 8 | Listing Angle | Ideal State (Should be 0°) | Operational State (<4° Normal), (>4° Alarm) |
Analyzing these data points helps operators understand crane behavior. It identifies inefficiencies and potential issues. This data-driven approach supports better decision-making. It optimizes operational strategies and resource allocation.
Remote Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance of Marine Deck Cranes
Remote monitoring capabilities are transforming crane management. Operators can supervise and control cranes from a centralized location. This enhances operational flexibility and reduces the need for on-site personnel. High-definition cameras and sensor feeds provide comprehensive real-time views of crane operations. This allows for immediate intervention if necessary.
Predictive maintenance is a direct benefit of IoT and AI integration. Instead of scheduled maintenance or reactive repairs, systems predict equipment failures. AI algorithms analyze sensor data for subtle changes or anomalies. These changes indicate impending issues. This allows maintenance teams to address problems before they cause downtime. Predictive maintenance minimizes unexpected breakdowns. It extends the lifespan of components. It also significantly reduces maintenance costs. This proactive strategy ensures maximum uptime and operational reliability for marine deck cranes.
Green Innovations Shaping Marine Deck Crane Design

The marine industry increasingly prioritizes environmental stewardship. This focus drives significant green innovations in marine deck crane design. Manufacturers develop solutions that reduce environmental impact while enhancing operational performance.
Energy Efficiency Enhancements for Marine Deck Cranes
Improving energy efficiency stands as a primary goal for green marine deck crane design. Engineers integrate advanced technologies to minimize power consumption. Regenerative energy systems capture and reuse energy generated during crane operations, such as lowering loads. This significantly reduces overall energy demand. Lightweight materials also contribute to efficiency. They decrease the crane’s structural weight, which in turn lowers the energy required for movement and operation. Electric driving technology, widely adopted in port cranes, also finds application in marine lifting equipment. This technology offers substantial energy savings compared to traditional diesel-hydraulic systems. Furthermore, a revolutionary closed hydraulic system reduces hydraulic oil consumption by over 50%. This innovation also significantly cuts power consumption, marking a major step forward in energy-efficient design.
Low and Zero-Emission Solutions in Marine Deck Cranes
The industry actively pursues low and zero-emission power sources for marine deck cranes. Hydrogen offers vast potential as a power source, with two main development streams: hydrogen combustion engines and fuel cells. Konecranes anticipates commercially available hydrogen-combustion engines and fuel cells within a couple of years. Fuel cells are considered more eco-efficient and cheaper to operate than combustion engines, despite their high initial capital outlay. They also envision a future where hydrogen could be generated locally at terminals to power cranes and even be sold to shipping companies.
Other solutions include electric motor-powered cranes. Liebherr, a crane manufacturer, states their electric motor-powered cranes can operate with a conventional electrical connection or ‘unplugged’ using batteries. This offers zero emissions and quiet operation. Liebherr actively develops battery electric drives, pooling technological skills at a ‘Battery Competence Centre’. Their ‘Unplugged’ series of crawler cranes are battery-powered and emissions-free, capable of working during charging. The Liduro Power Port, a battery-based mobile energy storage system from Liebherr, delivers up to 120 kW/kWh of electrical power. It supports fully electric or hybrid construction equipment, especially for sites without adequate power supply.
Alternative Fuel Adoption for Marine Deck Cranes
The adoption of alternative fuels represents another critical area of green innovation. Research into alternative fuels for marine deck crane propulsion, specifically for the ‘Sleipnir’ offshore crane vessel, focuses on liquid hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol. These are being investigated as hydrogen carriers for propulsion. The study emphasizes their technical feasibility, economic aspects, and health, safety, and environmental implications. Liquid hydrogen, stored at -253°C, requires thick insulation and has a lower energy density compared to ammonia and methanol. It is non-toxic but has a wide flammability range. Ammonia is widely available, with Wärtsilä researching its use in engines and MAN planning ammonia-fueled marine engines by 2025. Methanol is also widely available, with Maersk investing significantly in methanol-fueled ships and the Green Maritime Methanol consortium investigating its potential. These fuels aim to reduce carbon emissions by 2025.
Sustainable Materials and Lifecycle Management for Marine Deck Cranes
Manufacturers increasingly focus on sustainable materials and comprehensive lifecycle management for marine deck cranes. Lightweight materials are incorporated into marine deck cranes to improve energy efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint. This approach extends beyond operational efficiency to the entire product lifecycle. Manufacturers explore new materials that offer lower environmental footprints without compromising performance. Sustainability initiatives and environmental regulations drive this exploration. Lifecycle management involves designing cranes for durability, ease of maintenance, and eventual recycling. This minimizes waste and resource consumption throughout the crane’s operational life.
Market Drivers and Challenges for Marine Deck Crane Growth
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Mandates
Global regulations increasingly demand cleaner and more efficient maritime operations. These mandates push manufacturers and operators towards intelligent and green solutions. Compliance with environmental standards drives innovation in Marine Deck Crane design and functionality.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction Demands
The industry constantly seeks ways to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. New technologies deliver faster vessel turnaround times through high-capacity and automated systems. This leads to higher terminal productivity metrics. Optimized crane performance, achieved through smart sensors and predictive analytics, anticipates maintenance needs. Deck cranes with twin-lift spreaders and telescopic booms minimize vessel turnaround times, enhancing port productivity. These advancements result in long-term cost savings despite initial investments.
Enhanced Safety and Reliability Requirements
Safety remains paramount in marine operations. Advanced intelligent systems improve safety by reducing human error and providing real-time hazard detection. Predictive maintenance capabilities also enhance reliability, preventing unexpected breakdowns and ensuring continuous operation.
High Investment Costs for Advanced Marine Deck Cranes
Adopting advanced intelligent and green Marine Deck Cranes requires significant upfront capital. These high investment costs can deter some operators, especially smaller companies. However, the long-term operational savings and efficiency gains often justify these initial expenditures.
Skilled Labor Shortages in Marine Deck Crane Operations
The increasing complexity of modern Marine Deck Cranes demands a highly skilled workforce. A shortage of trained personnel capable of operating and maintaining these advanced systems poses a significant challenge for the industry.
Geopolitical and Supply Chain Factors Impacting Marine Deck Cranes
Geopolitical tensions can significantly impact maritime trade and oil and gas exploration activities. These global events often lead to reduced demand for deck cranes. Such tensions also influence the availability of raw materials and affect supply chain stability, impacting market growth and stability.
Impact on Key Marine Deck Crane Segments and Applications
Intelligent and green advancements significantly reshape operations across various marine sectors. These innovations enhance efficiency, safety, and environmental performance for specialized applications.
Commercial Shipping and Logistics Marine Deck Cranes
The commercial shipping sector demands highly efficient and reliable cargo handling. Operators require cranes to manage heavy containers, bulk cargo, and specialized equipment effectively. This reduces turnaround time and improves operational productivity. The industry adopts advanced crane technologies, including electro-hydraulic systems and automated controls. These systems provide enhanced precision, safety, and reliability. Integration of condition monitoring systems and remote operation capabilities minimizes downtime. It also optimizes performance in varying sea conditions. These versatile lifting solutions manage diverse cargo types and vessel sizes.
Offshore Wind Energy Sector Marine Deck Cranes
The offshore wind energy sector experiences rapid growth. This demands robust and precise lifting solutions. Marine deck cranes in this segment handle massive turbine components, foundations, and substations. Intelligent systems enable accurate placement and installation in challenging marine environments. Green technologies reduce the carbon footprint of these operations. They support the overall sustainability goals of renewable energy projects.
Military and Naval Marine Deck Cranes
Military and naval applications require highly specialized and durable marine deck cranes. These cranes perform critical tasks like cargo, stores, and ammunition handling. They also support Replenishment At Sea (RAS) operations for fuel and water. Suppliers like Allied Marine Crane provide marine duty hydraulic cranes and boat davits for various navies and coast guards. For example, they manufacture five deck cranes for the U.S. Coast Guard’s polar icebreaker Healy. Specific models include the GN 16-14 EH telescopic boom crane for TEU containers and the CHCD 6-25 EH stiff boom crane for cargo handling, which adheres to LR LAME Code and BS EN 13852 for personnel lifting.
Specialized Heavy Lift Marine Deck Crane Operations
Specialized heavy lift operations involve moving exceptionally large and heavy structures. These cranes feature immense lifting capacities.
| Vessel Name | Max. Capacity (ton) |
|---|---|
| Nan Tian Ma | 300 |
| … | … |
| Thialf | 12,000 |
| S 7000 | 14,000 |
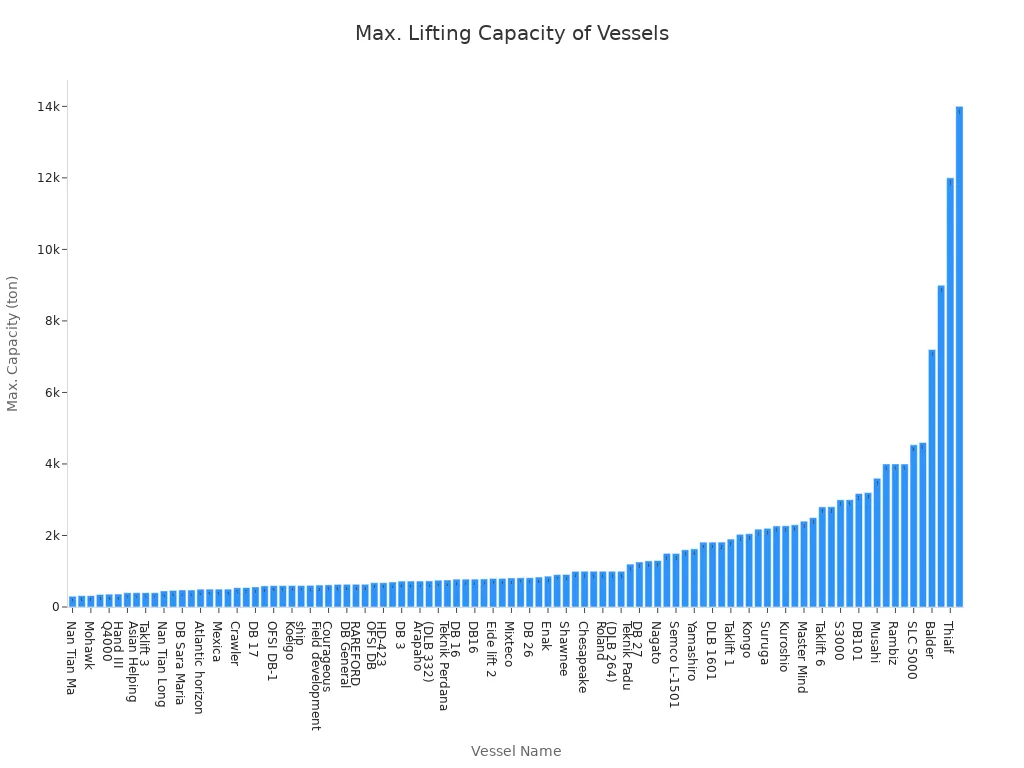
These vessels include semi-submersible crane vessels (SSCVs) like Saipem’s S7000 (14,000 tons) and Heerema’s Thialf (12,000 tons). Ship-shaped monohull lift vessels and sheer leg crane barges also perform these tasks. Most Heavy Lift Vessels (HLVs) lift between 500 and 1000 tons. Some reach up to 14,000 tons. These vessels are crucial for handling large subsea structures and reducing offshore hook-up costs.
Leading Players and Future Outlook for Marine Deck Cranes
The marine industry sees significant advancements from key players. These companies drive the future of lifting operations at sea. They focus on both smart technology and environmental responsibility.
Key Innovators in Intelligent Marine Deck Cranes
Several companies lead the charge in intelligent Marine Deck Crane technology. They integrate advanced AI, machine learning, and robotics into their systems. These innovators develop cranes with enhanced automation capabilities. They also focus on sophisticated sensor arrays and IoT connectivity. Their solutions enable predictive maintenance and remote operation. This improves efficiency and safety for maritime logistics. These companies continuously push boundaries. They aim for fully autonomous and highly optimized cargo handling operations.
Pioneers in Green Marine Deck Crane Solutions
Pioneers in green solutions actively reduce the environmental footprint of Marine Deck Cranes. Heerema’s ‘Sleipnir’ vessel stands out as the world’s most sustainable semi-submersible crane vessel. It operates on emission-reducing LNG and implements various other sustainability initiatives. Liebherr also actively develops green technology and products. This is a significant focus for their maritime cranes. Their efforts contribute to the advancement and competitiveness of the maritime industry. These companies invest in alternative fuels, electric drives, and energy recovery systems. They also explore sustainable materials and lifecycle management. Their innovations aim to meet strict environmental regulations. They also support a cleaner, more sustainable future for marine operations.
Intelligent and green advancements profoundly transform the Marine Deck Crane industry. These dual engines drive significant improvements in efficiency, safety, and environmental performance. The industry’s future trajectory clearly points towards increasingly sustainable and smart operations. This ensures a more responsible and productive maritime sector.
FAQ
What are the primary benefits of intelligent marine deck cranes?
Intelligent marine deck cranes offer enhanced precision, improved safety through hazard detection, and optimized operational efficiency. They also enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs.
How do green innovations contribute to marine deck crane sustainability?
Green innovations reduce environmental impact through energy efficiency, lower emissions, and alternative fuel adoption. They also promote sustainable materials and lifecycle management, supporting a cleaner maritime industry.
What challenges does the industry face in adopting intelligent and green marine deck cranes?
The industry faces high investment costs for advanced systems and a shortage of skilled labor. Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions also impact market growth and stability.